Welcome to the LED Learning Center
Behind the Scenes
Daktronics Display Components and Their Working Parts
Daktronics products come in all different shapes and sizes. Message displays, video boards and scoreboards are made up of similar components that work together to create the big picture.
What is an LED?
A light emitting diode (LED) is a tiny, electronic semiconductor that converts electric energy into visible light. The chemical compound used within an LED determines its color, brightness and power efficiency.
Unlike incandescent lamps, LEDs have no filaments that can burn out or fail.
Index
Jump to the Answers
LEDs Come in Four Different Forms
Manufacturers use several types of LEDs to construct digital displays. The four most common are Through-Hole LEDs, Surface Mount Device (SMD) also known as Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Integrated Matrix Devices (IMD), and Flip-Chip Chip on Board (FC COB). Each type has its respective advantages that make them preferable for different applications.

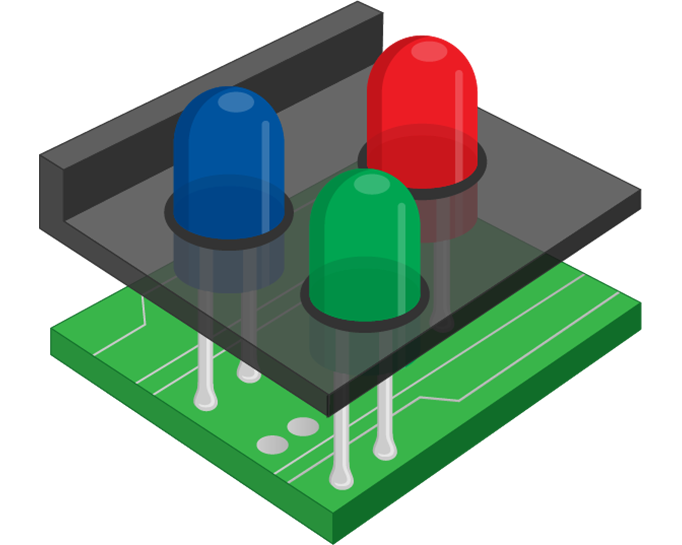
Integrated Matrix Device
Integrated Matrix Device (IMD) LED components consist of RGB pixels mounted on a common substrate, often in a 2x2 array. Extra tinting and texturing provides 2.5X more solder bonding area than traditional SMD technology.
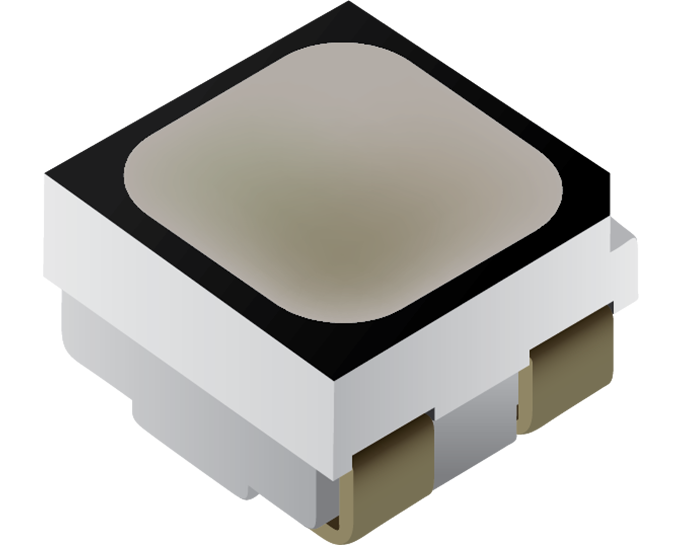

Surface Mount LEDs
Surface Mount Devices, or SMD for short, refers to the LED lead frame mounting method. LEDs are mounted to the surface of the circuit board. The SMD contains red, green and blue die.
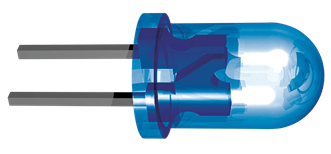
Through-Hole LEDs
Through-hole LEDs are mounted with leads protruding through the circuit board and appear to stand taller. Each LED is a single-color die of either red, green or blue.
Chip on Board LEDs
Chip on Board (COB) modules have red, blue, and green LEDs directly mounted to the circuit board, eliminating the need for wire bonds and the traditional packaging used for SMD and IMD LEDs.
IMD LEDs
IMD LEDs, known for their compact size, feature red, green, and blue LEDs arranged in a 2x2 packaged array. Each package contains a total of 12 LEDs which helps produce high-quality imagery and refines fine details. Due to the higher LED count, products incorporating IMD typically start at a higher price point compared to those using SMD LEDs.
Benefits of IMD:
- Tighter pixel densities
- Durable (2.5x strength compared to SMD)
- Improved contrast
- Anti-Glare
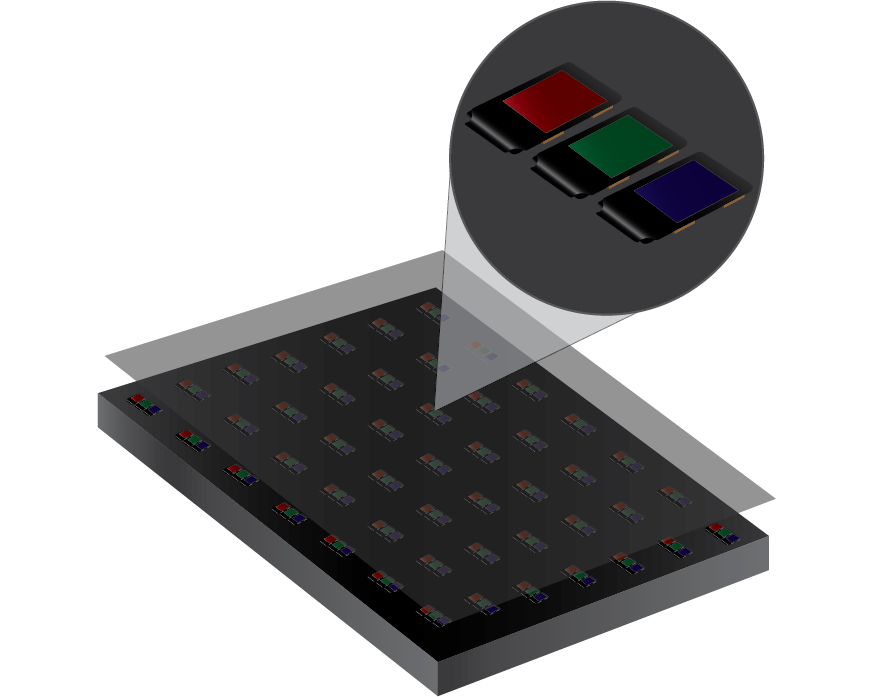
SMD LEDs
Total light emitted isn't concentrated in a focused area since SMD LEDs do not have directional reflector cups. Instead light disperses evenly across both horizontal and vertical angles, providing wider viewing angles. This makes SMD LEDs an excellent choice for most indoor applications as well as some tighter pitch outdoor applications.
Benefits of SMD:
- Outstanding color blending at short viewing distance
- No color shift at extreme angles
- Wide viewing angle
Through-Hole LEDs
Through-hole LEDs use a reflector cup and an epoxy lens package. This combination as well as the type of die used, plays a role in determining the elliptical viewing cone produced. A through-hole LED's reflector cup focuses the light emitted by the die into a specific viewing area.
Benefits of Through-Hole:
- Optimized for moderate to longer viewing distance
- Louvers deflect sunlight for higher contrast
- Black matte finish reduces reflection
- Brighter than SMD LEDs
Chip on Board LEDs
This emerging LED technology involves directly mounting RGB LEDs onto the display’s surface. The direct mounting approach enhances the display's black state, thereby increasing contrast compared to other LED technologies. Additionally, COB LEDs operate at cooler temperatures, consume less power, and incorporate a deep-black surface barrier for encapsulation and protection against external damage. These features make them suitable for installation in a variety of lighting conditions and close-encounter environments.
Benefits of COB:
- Highest contrast
- Consumes less power
- Shielded LEDs perfect for close-encounter environments
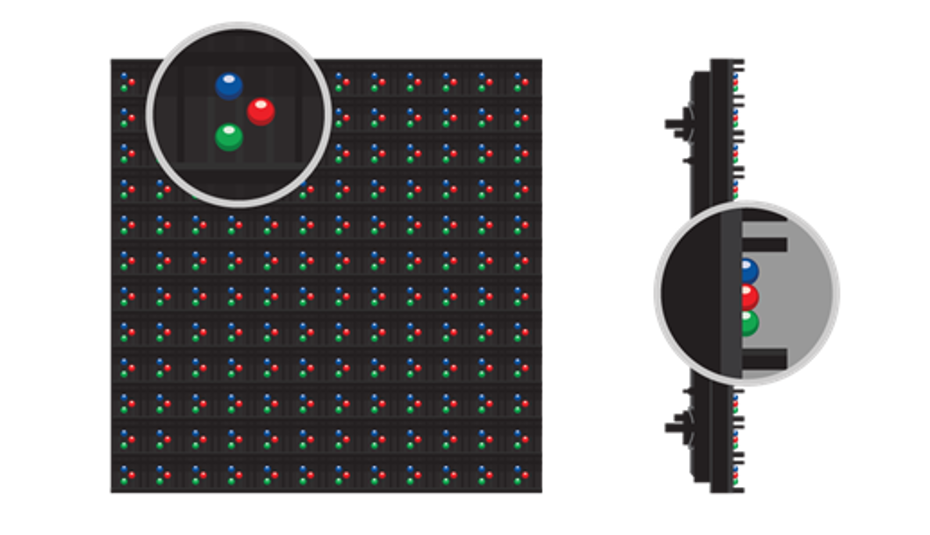
What is a module?
LED modules are made up of parts that form the building blocks of video displays, message centers and dynamic message signs. Rows of modules line together to arrange the LEDs in different variations depending on their product, market and purpose.
How Daktronics Does It Best
Daktronics modules are designed for ease of service and installation. Whether your display is standard or custom, our modules are sure to fit your needs.

What is a digit?
A digit is a numeric symbol with seven segment bars. Each segment uses discrete LEDs to produce a value between 0-9. Scoreboards, timing systems and price displays use digits to display information.
How Daktronics Does It Best
Daktronics digit components offer high-contrast, full-height, broad-stroke digits that provide clear and highly legible numeric information.
What is a pixel?
Pixels, short for picture elements, are points of light that illuminate to form letters, words, graphics, animations and video images. A pixel can be made up of a single LED, multiple LEDs of the same color or multiple LEDs of different colors. They are the smallest elements of the electronics display system that can be individually controlled and turned off or on at various brightness levels.
How Daktronics Does It Best
When our engineers design displays, they evaluate the number of LEDs necessary in each pixel to obtain the necessary brightness, while keeping cost and power efficiency in mind for you, our customers.
4 mm Pixel Pitch
![]()
16 mm Pixel Pitch
![]()
26 mm Pixel Pitch
![]()
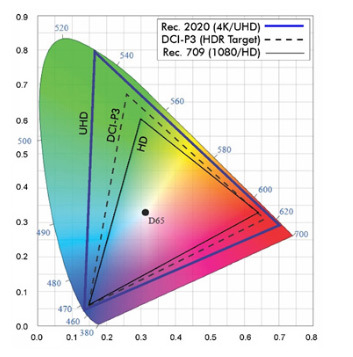
Life-like image quality for digital technology
HDR, or High Dynamic Range imaging is the production, transfer and display of content containing a much wider range of color and contrast than historically available. An SDR display can produce 16.7 million colors, while an HDR display can produce 1.07 billion colors. It’s the closest match to how you see colors and detail in real life.
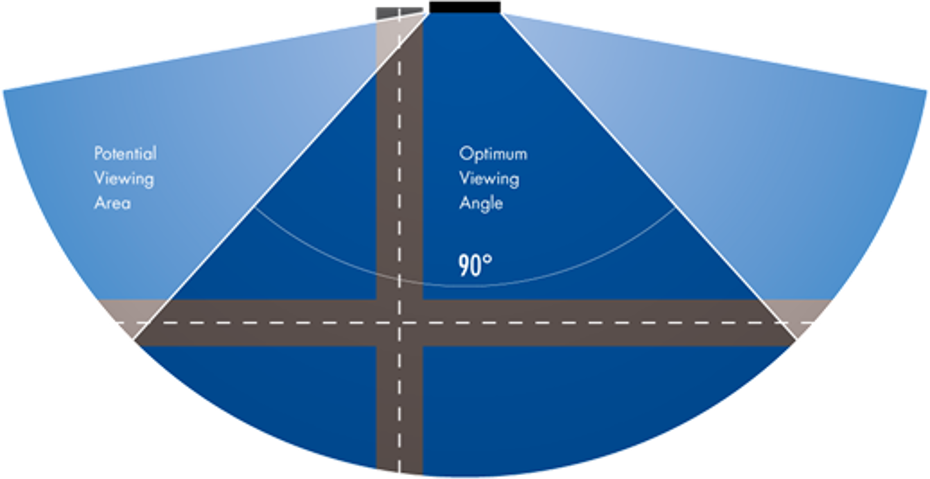
The Viewing Cone
When choosing a display, consider where it will be installed and the angle at which the display will be viewed. Image quality will be at it's best within the viewing cone of the display—where your primary intended audience should be located.
Readability angle or viewing area will exceed the optimum viewing angle depending on site-specific circumstances and ambient light conditions.
What are viewing distances?
Viewing distances are calculated based on the display type and the distance from the display. Each display will have a minimum and a maximum viewing distance that may vary based on application and intended use.
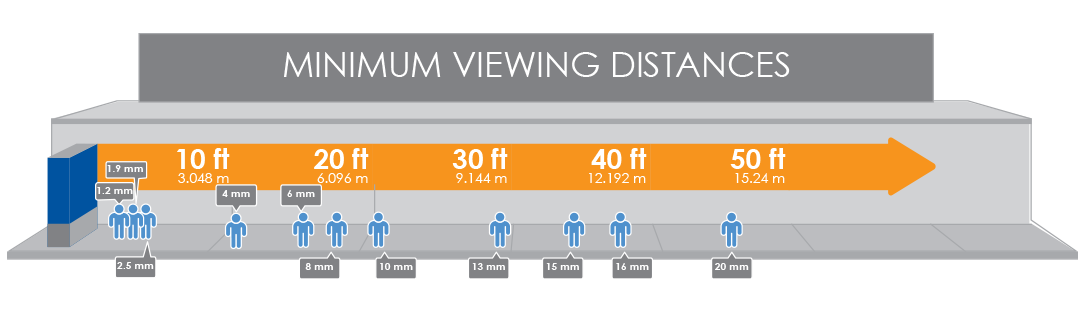
A large character will have a longer viewing distance while a small character will have a shorter viewing distance. Language will also bring some variance in character size recommendations. For example: the character size should be at least 1/300th of the viewing distance for English text, 1/150th of the viewing distance for Traditional Chinese characters, and 1/200th for Simplified Chinese characters.
Character spacing, also known as pixel pitch, will vary between indoor and outdoor display applications.
Want to learn more? We're here to help.
Let our experts answer questions about the benefits of products customized for you.